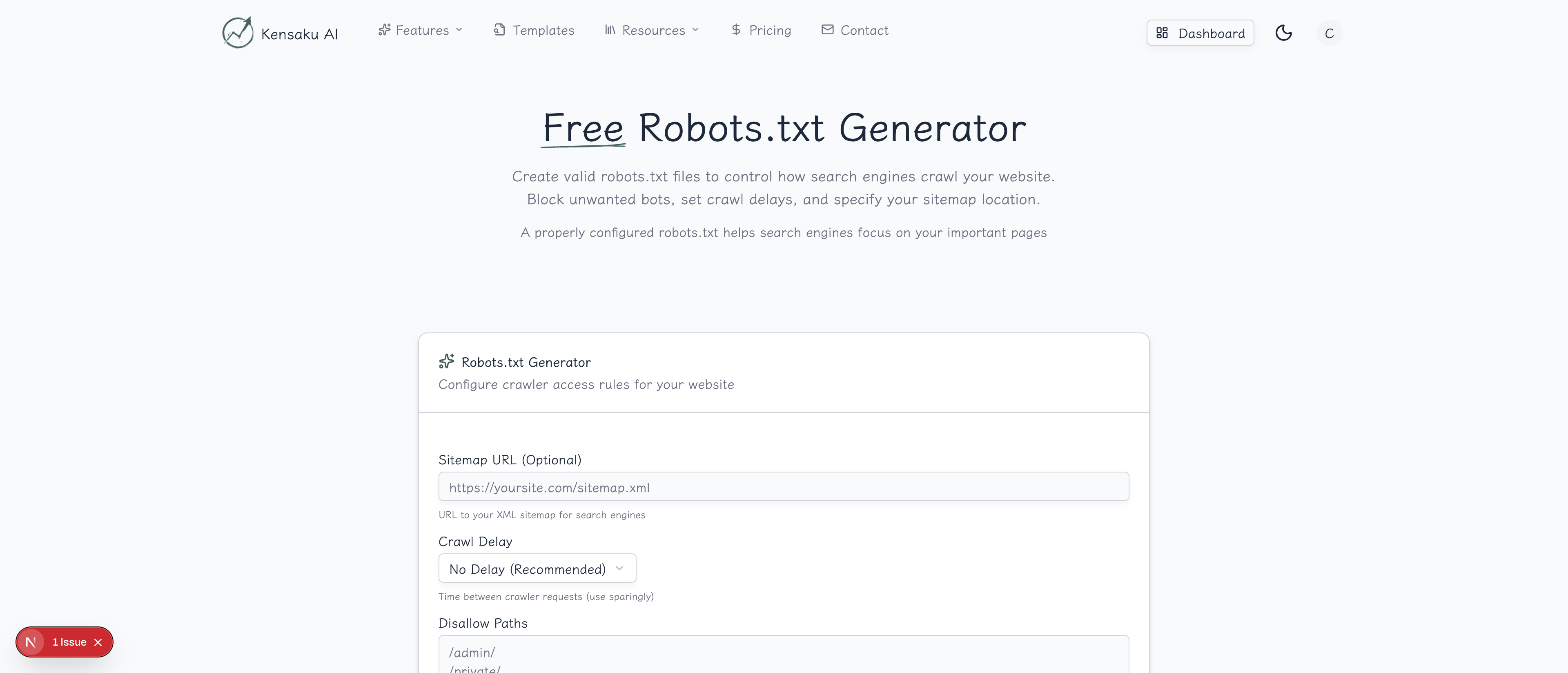
Your robots.txt file is the first thing search engines read when they visit your site. A misconfigured robots.txt can accidentally block important pages from being indexed—or worse, expose sensitive directories to crawlers. Getting it right matters.
Our free Robots.txt Generator creates properly formatted robots.txt files with the exact directives you need, helping you control crawler access without the syntax headaches.
What is Robots.txt?
Robots.txt is a text file placed in your website's root directory that tells search engine crawlers which pages or sections they can and cannot access. It follows the Robots Exclusion Protocol—a standard that all major search engines respect.
A typical robots.txt file looks like:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /private/
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xmlWhy Robots.txt Matters
Crawl Budget Optimization
Search engines allocate limited crawling resources to each site. By blocking unimportant pages, you ensure crawlers focus on your valuable content:
- Block admin areas and login pages
- Exclude duplicate content paths
- Prevent crawling of search result pages
- Hide staging or development directories
Security Through Obscurity
While robots.txt doesn't provide real security (anyone can ignore it), it prevents:
- Search engines from indexing sensitive URLs
- Automated tools from discovering admin panels
- Internal tools appearing in search results
Preventing Duplicate Content
Block crawler access to:
- URL parameters that create duplicates
- Print-friendly page versions
- Sorted or filtered listing pages
- Session-specific URLs
Sitemap Declaration
Robots.txt is the standard place to declare your sitemap location, helping search engines discover all your pages efficiently.
How the Generator Works
Step 1: Choose Your Base Configuration
Select a starting point:
| Preset | Description |
|---|---|
| Allow All | Permits all crawlers everywhere |
| Standard | Common blocks for admin, private |
| Restrictive | Blocks most areas, allows specific paths |
| Custom | Start from scratch |
Step 2: Configure User-Agents
Specify which crawlers your rules apply to:
*(asterisk): All crawlers- Googlebot: Google's main crawler
- Bingbot: Microsoft's Bing crawler
- GPTBot: OpenAI's crawler
- Specific bots: Target individual crawlers with different rules
Step 3: Set Allow and Disallow Rules
Define what each crawler can access:
Disallow rules block access:
/admin/- Blocks entire admin directory/private/- Blocks private section/*.pdf$- Blocks all PDF files/search- Blocks search result pages
Allow rules permit access (useful with wildcards):
/public/- Explicitly allows public folder/*.css- Allows CSS files even if parent blocked
Step 4: Add Your Sitemap
Include your sitemap URL(s) for crawler discovery:
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap-posts.xml
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap-products.xmlStep 5: Generate and Implement
Click "Generate" to create your robots.txt. Copy the output and save it as robots.txt in your site's root directory.
Robots.txt Syntax Guide
User-Agent Directive
Specifies which crawler the following rules apply to:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /private/
User-agent: *
Disallow: /admin/Disallow Directive
Blocks access to specified paths:
Disallow: /admin/ # Blocks /admin/ and everything inside
Disallow: /page.html # Blocks specific file
Disallow: / # Blocks entire site
Disallow: # Blocks nothing (allows all)Allow Directive
Permits access, useful for exceptions:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /folder/
Allow: /folder/public/ # Exception within blocked folderWildcards
Pattern matching for flexible rules:
Disallow: /*.pdf$ # All PDFs
Disallow: /*? # URLs with query strings
Disallow: /*/private/ # 'private' folder anywhere
Allow: /*.js$ # All JavaScript filesCrawl-Delay
Request crawlers wait between requests (not supported by Google):
User-agent: Bingbot
Crawl-delay: 10 # Wait 10 seconds between requestsCommon Robots.txt Configurations
Standard Website
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Disallow: /admin/
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Disallow: /login/
Disallow: /cart/
Disallow: /checkout/
Disallow: /account/
Disallow: /*?s=
Disallow: /*?p=
Disallow: /search/
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xmlE-commerce Site
User-agent: *
Allow: /
Disallow: /cart/
Disallow: /checkout/
Disallow: /account/
Disallow: /wishlist/
Disallow: /*?sort=
Disallow: /*?filter=
Disallow: /*?page=
Disallow: /internal/
Disallow: /admin/
User-agent: Googlebot-Image
Allow: /images/products/
Disallow: /images/internal/
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap.xml
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap-products.xmlWordPress Site
User-agent: *
Allow: /wp-content/uploads/
Disallow: /wp-admin/
Disallow: /wp-includes/
Disallow: /wp-content/plugins/
Disallow: /wp-content/themes/
Disallow: /trackback/
Disallow: /feed/
Disallow: /comments/
Disallow: /*?s=
Disallow: /*?p=
Disallow: /author/
Disallow: /tag/
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap_index.xmlBlocking AI Crawlers
Many sites now block AI training crawlers:
User-agent: GPTBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: ChatGPT-User
Disallow: /
User-agent: CCBot
Disallow: /
User-agent: anthropic-ai
Disallow: /
User-agent: Google-Extended
Disallow: /
User-agent: *
Allow: /Programmatic SEO Considerations
Managing Thousands of Pages
For programmatic SEO sites with many generated pages:
User-agent: *
Allow: /
# Block test/staging patterns
Disallow: /test-*
Disallow: /staging/
Disallow: /preview/
# Block low-value generated pages
Disallow: /*?ref=
Disallow: /*?utm_
Disallow: /empty-*
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap-index.xmlFaceted Navigation
E-commerce sites with filters need careful configuration:
# Allow category pages
Allow: /products/
# Block filtered variations
Disallow: /*?color=
Disallow: /*?size=
Disallow: /*?sort=
Disallow: /*?page=
# But allow specific valuable filters
Allow: /*?category=Dynamic Sitemap References
For large sites with multiple sitemaps:
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap-main.xml
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap-products.xml
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap-locations.xml
Sitemap: https://example.com/sitemap-blog.xmlTesting Your Robots.txt
Google Search Console
Test specific URLs against your robots.txt:
- Go to Search Console
- Use the URL Inspection tool
- Check "Crawl allowed?" status
robots.txt Tester
Google's tester (in Search Console) shows:
- Syntax errors
- Blocked URLs
- Which rules apply to which bots
Common Testing Checklist
- Important pages are NOT blocked
- Admin areas ARE blocked
- Sitemap URL is correct and accessible
- No syntax errors
- Rules work for intended user-agents
Common Robots.txt Mistakes
Blocking Your Entire Site
Disaster:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /This blocks all crawlers from your entire site. Your pages will be deindexed.
Blocking CSS/JS Files
Problematic:
Disallow: /wp-content/This blocks CSS and JavaScript, preventing Google from rendering your pages correctly.
Better:
Disallow: /wp-content/plugins/
Allow: /wp-content/themes/
Allow: /wp-content/uploads/Conflicting Rules
Confusing:
Disallow: /folder/
Allow: /folder/Be consistent. The last matching rule typically wins, but behavior varies by crawler.
Forgetting the Trailing Slash
Different meanings:
Disallow: /admin # Blocks /admin, /admin.html, /administrator
Disallow: /admin/ # Blocks only /admin/ directoryTreating Robots.txt as Security
Robots.txt is public and doesn't prevent access—it just asks crawlers to respect your wishes. For real security, use authentication.
Robots.txt vs. Meta Robots
| Feature | Robots.txt | Meta Robots |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Entire directories | Individual pages |
| Location | Root directory | Page <head> |
| Prevents crawling | Yes | No (page must be crawled to read tag) |
| Prevents indexing | Indirectly | Yes (noindex) |
| Flexibility | Path-based | Page-specific |
Use robots.txt for broad rules, meta robots for page-specific control.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular Audits
Review your robots.txt when:
- Adding new site sections
- Launching new features
- Changing URL structure
- Noticing indexing issues
Search Console Monitoring
Watch for:
- Crawl errors related to blocked resources
- Pages unexpectedly excluded from index
- Coverage issues mentioning robots.txt
Version Control
Keep your robots.txt in version control:
- Track changes over time
- Roll back problematic updates
- Document why rules exist
Integration with SEO Workflow
Build robots.txt management into your process:
- Site architecture planning → Define what should be crawled
- Robots.txt Generator → Create initial configuration
- Testing → Verify important pages accessible
- Deployment → Place in root directory
- Monitoring → Watch Search Console for issues
- Iteration → Update as site evolves
Get Started
Ready to take control of how search engines crawl your site? Try our free Robots.txt Generator now.
For teams managing complex sites with programmatic SEO, explore our full platform with automated technical SEO tools and bulk page management.